COVID-19 ECONOMIC RECESSION
RECESSUS / RECESSION
(A nickel ain't worth a dime anymore)
-Yogi Berra
Post by: Sarvesh and Sharvari, Commerce Students
JOIN THE DISCUSSION ON OUR WHATSAPP GROUP AND REDDIT
For a millenia, the people of Britain had been using bronze to make tools, jewellery and currency for trade. But around 800 BCE, that began to change as the value of bronze declined causing social upheaval and economic crisis what we would call a RECESSION.
A recession is generally a downturn in any economy associated with high unemployment, slowing gross domestic product, high inflation and many such factors.
What causes recessions?
Recessions occur when there is a negative disruption to the balance between demand and supply, there is a mismatch between how many goods people want to buy, how many products and services can the producer offers and the price of these commodities are sold which prompts an economic demand.
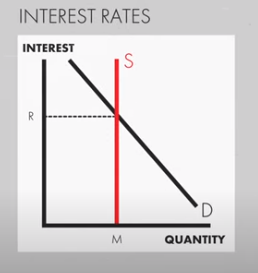
An economy's relationship between supply and demand is reflected in its inflation and interest rates.
Inflation happens when goods and services get more expensive, or the value of money decreases. Still, inflation isn't necessarily a bad thing. But high inflation rates that aren't accompanied by high demand can cause problems for the economy and eventually lead to a recession.
When interest rates rise, they limit liquidity, which is money available to invest. In the past, the biggest culprit was the Federal Reserve, which often raised interest rates to protect the value of the dollar. For example, the Fed raised interest rates during the 1970s, which contributed to the 1980 recession.
Reduced consumer confidence is another factor that can cause a
recession. If consumers believe the economy is bad, they are less likely to
spend money. Consumer confidence is psychological but can have a real impact on
any economy.
Reduced real wages, another factor, refers to wages that have
been adjusted for inflation. Falling real wages means that a worker's paycheck
is not keeping up with inflation. The worker might be making the same amount of
money, but his purchasing power has been reduced.
Natural calamities or a pandemic may also cause a recession(which is happening now).
GLOBAL RECESSION
A global recession is that which affects many countries around the world, that is, a period of global economic slowdown or declining economic output.
The IMF defines a global recession as "a decline in annual per‑capita real World GDP backed up by a decline or worsening for one or more of the seven other global macroeconomic indicators: Industrial production, trade, capital flows, oil consumption, unemployment rate, per‑capita investment, and per‑capita consumption".
There were six global recessions since 1970: 1974–75, 1980–83, 1990–93, 1998, 2001–02, and 2008-09.
THE GREAT RECESSION
There were many leading factors which predicted but the effect was felt much later. From the period of 1977 to 2006, people recklessly bought houses. They were given loans though they didn't have the credibility to pay back with higher interest rates in the future. The lenders handed them an adjustable-rate mortgage, which lent loans at lower rates and then increases rate sky high. In 2006 the prices dropped drastically and the value came so low that even after selling the house, the loan couldn't be paid back. The loaning companies and its investors worldwide were under a dramatic loss. The shift in the cycle was unrecognized.
The investors do not recognise the turn of events and we as an economy keep forgetting that it cannot grow forever
History repeats...we have to fall to rise again.
CORONAVIRUS RECESSION
The Coronavirus recession, also known as the Great Lockdown or Great Shutdown, is an ongoing severe global economic recession which began affecting the world economy on 20 February 2020 with the 2020 stock market crash and significantly worsened during the pandemic. The recession has been the steepest economic downturn since the Great Depression. Great Lockdown
The IMF has stated that the economic decline is "far worse" than that of the Great Recession in 2009. The pandemic has led to more than a third of the world's population being placed on lockdown to stop the spread of the virus. This has caused severe economic repercussions for economies across the world.
RECESSION AND GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT
An economic recession is typically defined as a decline in the Gross Domestic Product(GDP) for two or more consecutive quarters. GDP is the market value of all goods and
services produced within a country in a given period of time.
The below chart represents the GDP growth of the past, present and next year. This is a major lagging indicator.
IMF expects global growth to rebound to 5.8% next year if the pandemic fades in the second half of 2020.
The bronze recession in Britain eventually ended when the adoption of iron helped revolutionize farming and food production. Modern markets are more complex making today's recession far more difficult to navigate but each recession provides new data to help anticipate and respond to future recession more effectively.
What could be the major take away this time?
Let's find out in the next posts!!
JOIN THE DISCUSSION ON OUR WHATSAPP GROUP AND REDDIT
References:






It's nice bro ND kept up
ReplyDeleteGreat information...keep updating!!..:)
ReplyDeleteElaborate on impact of Covid 19
ReplyDeleteWill work with that in the upcoming posts
DeleteEvery part was clear and precise grt work
ReplyDeleteExcellent explanation
ReplyDeleteI didn't know the reason of recession till now
Thank you
Very informative,
ReplyDelete