MACROPRUDENTIAL REGULATION WILL DAMPEN THE EFFECT OF GLOBAL FINANCIAL SHOCKS
POST BY: Sarvesh
The COVID-19 pandemic is impacting emerging markets through an unprecedented combination of domestic and external shocks. Among the latter, the pandemic has led to a sharp
increase in global risk aversion and an abrupt retrenchment in foreign capital
flows. Based on historical experience, these types of global financial shocks
can significantly affect macroeconomic conditions in emerging markets, even if
the exchange rate is flexible.
FOR MORE UPDATES ON OUR BLOG, JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP AND REDDIT PAGE
Strengthening resilience with macroprudential
regulation
Macroprudential regulation involves a broad range of measures aimed at buttressing financial stability. While strengthening financial
stability can also dampen the impact of global financial shocks on economic
activity in emerging markets.
What is macroprudential regulation?
Macroprudential
regulation is an approach to financial regulation, aiming to mitigate risk
to the entire financial system and thus avoiding and reducing the macroeconomic
costs of financial instability. The approach is used by central banks and
regulators around the world. One example of macroprudential policy is the higher capital charge applied to banks that pose more risk to the system.
Another example, in a macroprudential framework, the ability of a bank to increase its capital
to meet regulatory requirements is seen as favourable, without regard to how
this is accomplished. But a bank that needs to increase
its capital ratio (measured as a percentage of its asset) can either raise new
capital or decrease assets (loans). When bank losses are
increasing because the economy is weak and bank capital ratios are falling, The difference between the two approaches is consequential. If every firm were to
decrease assets instead of raise capital, that action would lead to a
substantive contraction of credit and cause the economy to weaken further. A macroprudential
approach, in contrast, would assess and control for the mechanism that banks
would implement to reach their required capital ratio, essentially encouraging them to raise capital rather than pull back on
lending.
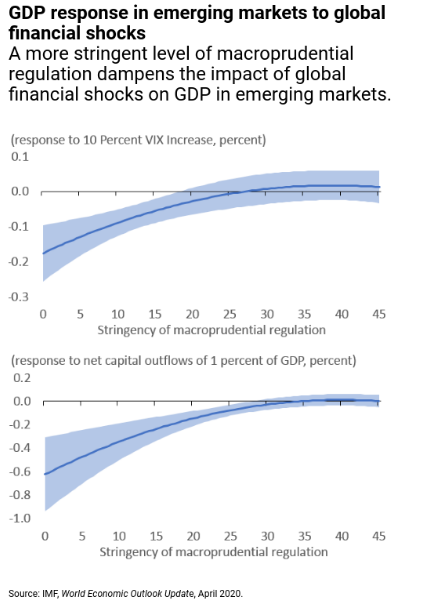
If the level of macroprudential regulation is
low, an increase in global risk aversion (proxied by the Chicago Board Option
Exchange Volatility Index (VIX)) or outflow of foreign capital considerably
reduces economic growth in emerging markets. These negative effects become less
pronounced in countries with tighter levels of macroprudential regulation. In
fact, if the level of regulation is sufficiently stringent, global financial
shocks do not seem to have a significant impact on GDP growth in emerging
markets.
These
dampening effects are symmetric. That is, macroprudential regulation reduces
the sensitivity of domestic activity to both positive and negative global
financial shocks. Therefore, tighter macroprudential regulation prevents
sharper economic slowdowns when global financial conditions tighten, but it
comes at the cost of foregone economic activity when global financial
conditions are favourable. This calls for more research on how to optimally
adjust macroprudential regulation over time depending on both domestic and
foreign developments.
Macroprudential regulation to support
We
also, examine whether the level of macroprudential regulation influences the
monetary policy response to global financial shocks. In several emerging
markets, central banks tend to increase policy rates when global financial
conditions tighten, possibly because of financial stability concerns arising
from capital outflows and the depreciation of the exchange rate. In these
cases, monetary policy appears to react pro-cyclically, likely .
This analysis shows that macroprudential regulation can play an important role in favouring a more countercyclical response to monetary policy. If the level of macroprudential regulation is low, we find that central banks tend to increase policy rates when US monetary policy tightens or the VIX increases. On the contrary, if macroprudential regulation is more stringent—thereby alleviating financial stability concerns—monetary policy responds countercyclically. When US monetary policy tightens and the VIX increases, central banks tend to reduce policy rates, thus cushioning the impact on the domestic economy.
More analysis is needed
There are important caveats to the analysis. First, available measures of macroprudential regulation suffer from several drawbacks, for example, because they generally fail to capture the intensity of changes in regulation. Therefore, the chapter’s empirical findings will need to be re-assessed as more refined measures become available. Second, it will be important to test for the robustness of the findings using empirical specifications that allow for a richer interplay of macroprudential regulation with other policy tools, especially capital flow management measures and foreign exchange intervention.
Macroprudential policies alongside monetary policy should be strictly implemented in economies to dampen this COVID-19 recession.
FOR MORE UPDATES ON OUR BLOG, JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP AND REDDIT PAGE
References:





Thanks for the interesting read. The COVID-19 pandemic sure had a strong effect on the stock market. The Dow Jones had a huge decrease because of the pandemic. People sure now think that stocks are even more risky at this time. It would be nice to have more financial stability as soon as possible.
ReplyDeleteI get your explanation that some banks may "pose more risk for the system." A strong bank needs to have many assets, as I understand it. I get that banks are offered more loans by government (more loans offered just because of pandemic crisis). But, being able to get more loans is not really strengthening the banks. Yeah, sooner or later those loans have to be paid back.
Weird that some systems exist that are "forever in debt." Some things are a never ending cycle of debt. Somehow, all this has to work.
I hope the economic situation can be improved during the COVID-19 recession.
Check out Economy and Stock Market News. Read interesting latest news about world, business, investments, marketing, advertising, funny moments and more. Take a look at Canada Forums for interesting Canadian news.